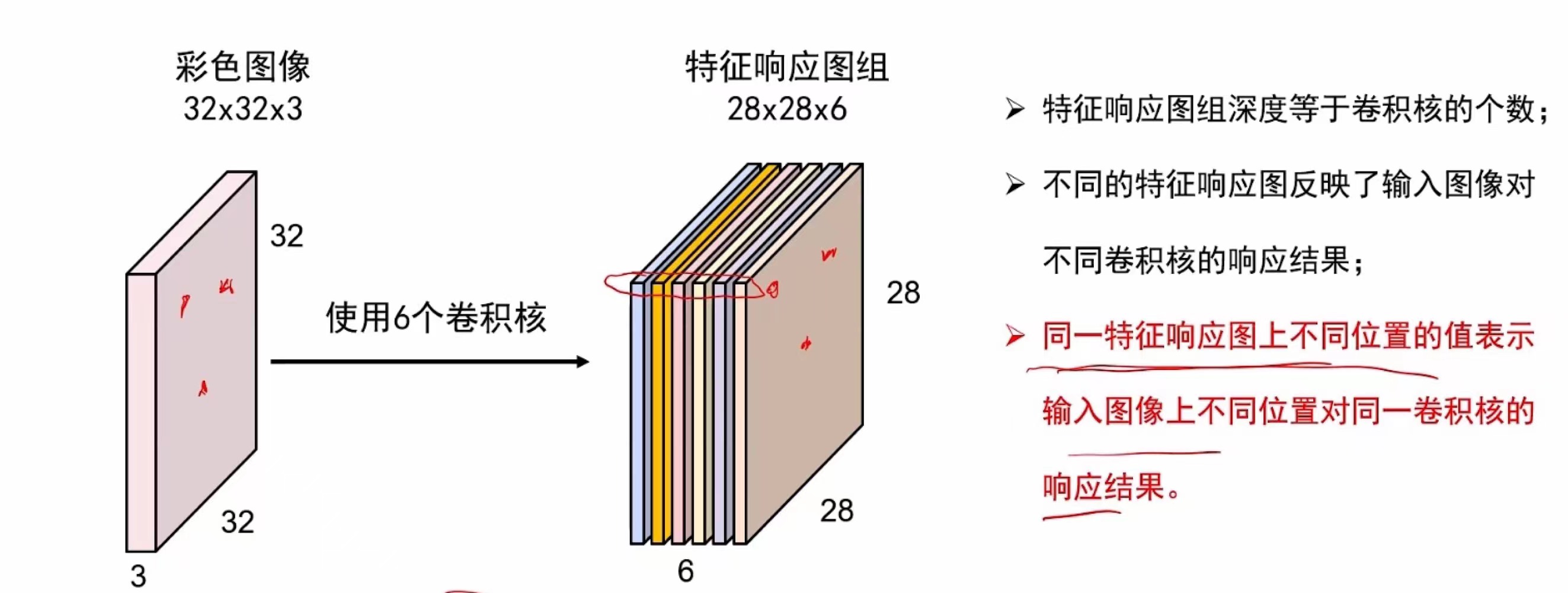
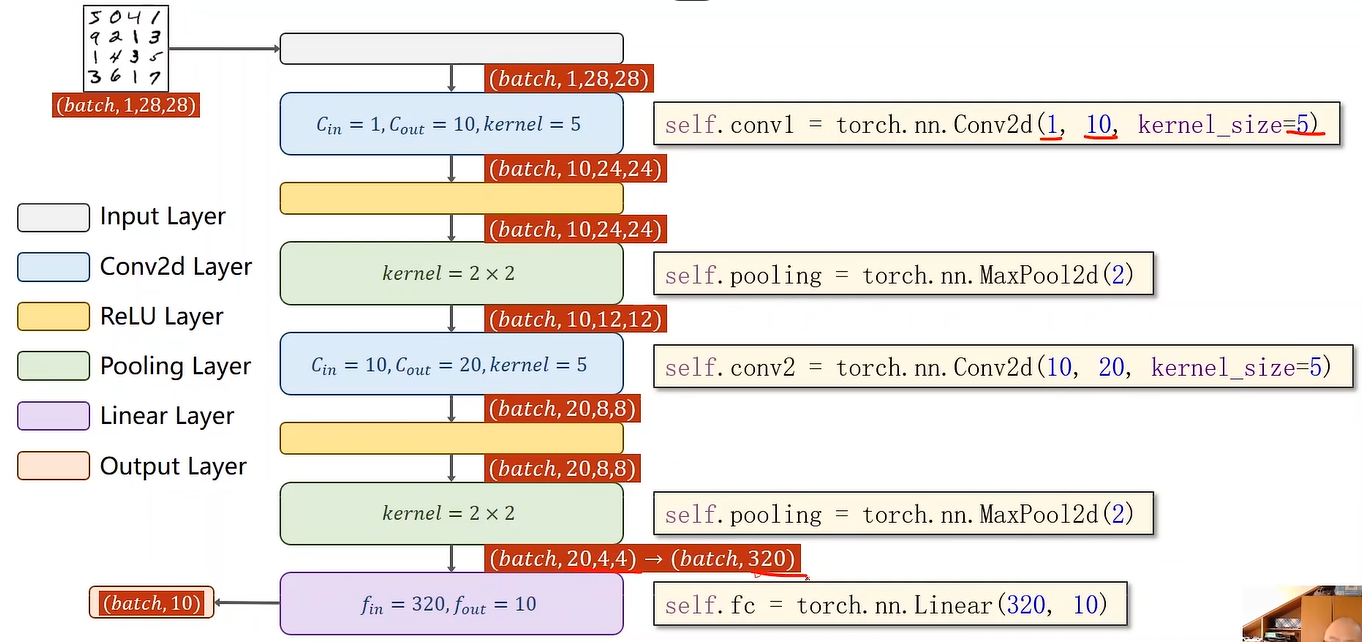
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
| import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
batch_size = 64
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(), #把图像转化为张量
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,),(0.3081,)) #mniset常用均值标准差
])
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist',
train = True,
download = True,
transform = transform)
trainloader = DataLoader(train_dataset,
shuffle = True,
batch_size=batch_size)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='../dataset/mnist',
train = False,
download = True,
transform = transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset,
shuffle=False,
batch_size=batch_size)
# 有GPU使用GPU
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 定义卷积神经网络
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.pooling = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(320, 10)
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.size(0)
x = F.relu(self.pooling(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.pooling(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(batch_size, -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# 实例化模型并移动到 GPU
model = Net().to(device)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.01,momentum=0.5) #momentum冲量
train_losses = []
test_accuracies = []
def train(epoch):
running_loss = 0.0
for batch_size, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
inputs, target = data
inputs,target = inputs.to(device),target.to(device) # 把inputs和targets也传至GPU
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
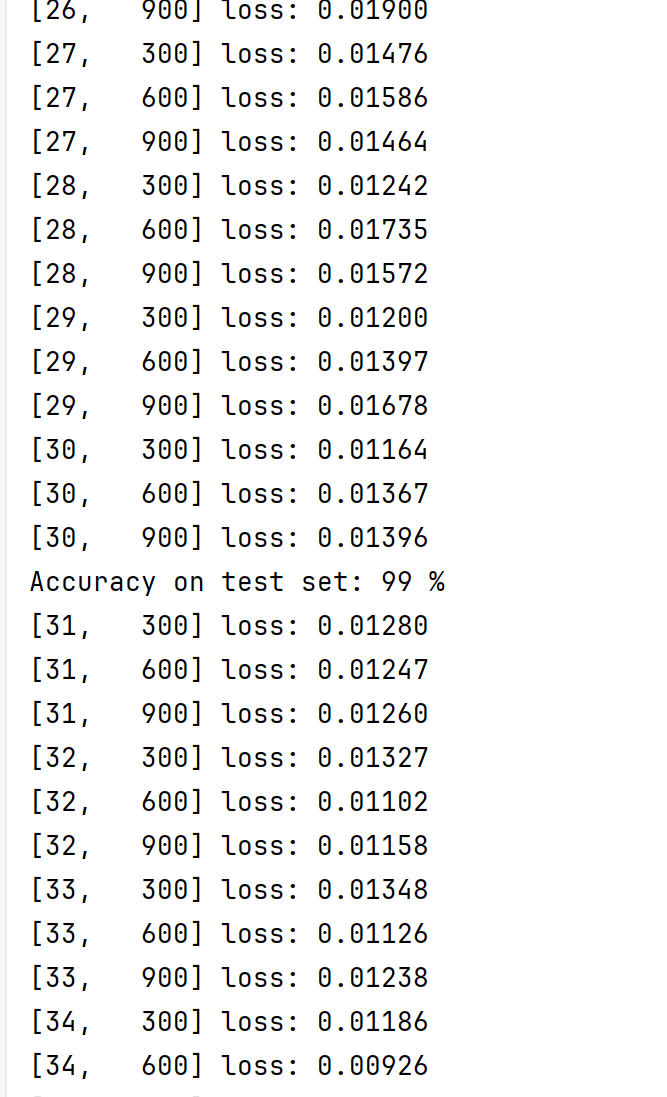
if batch_size % 300 == 299:
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.5f' % (epoch + 1, batch_size + 1, running_loss / 300))
running_loss = 0.0
train_losses.append(running_loss / len(trainloader))
def test():
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_loader:
images, labels = data
images,labels = images.to(device),labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
accuracy = 100*correct /total
test_accuracies.append(accuracy)
print('Accuracy on test set: %d %%' % (100 * correct / total))
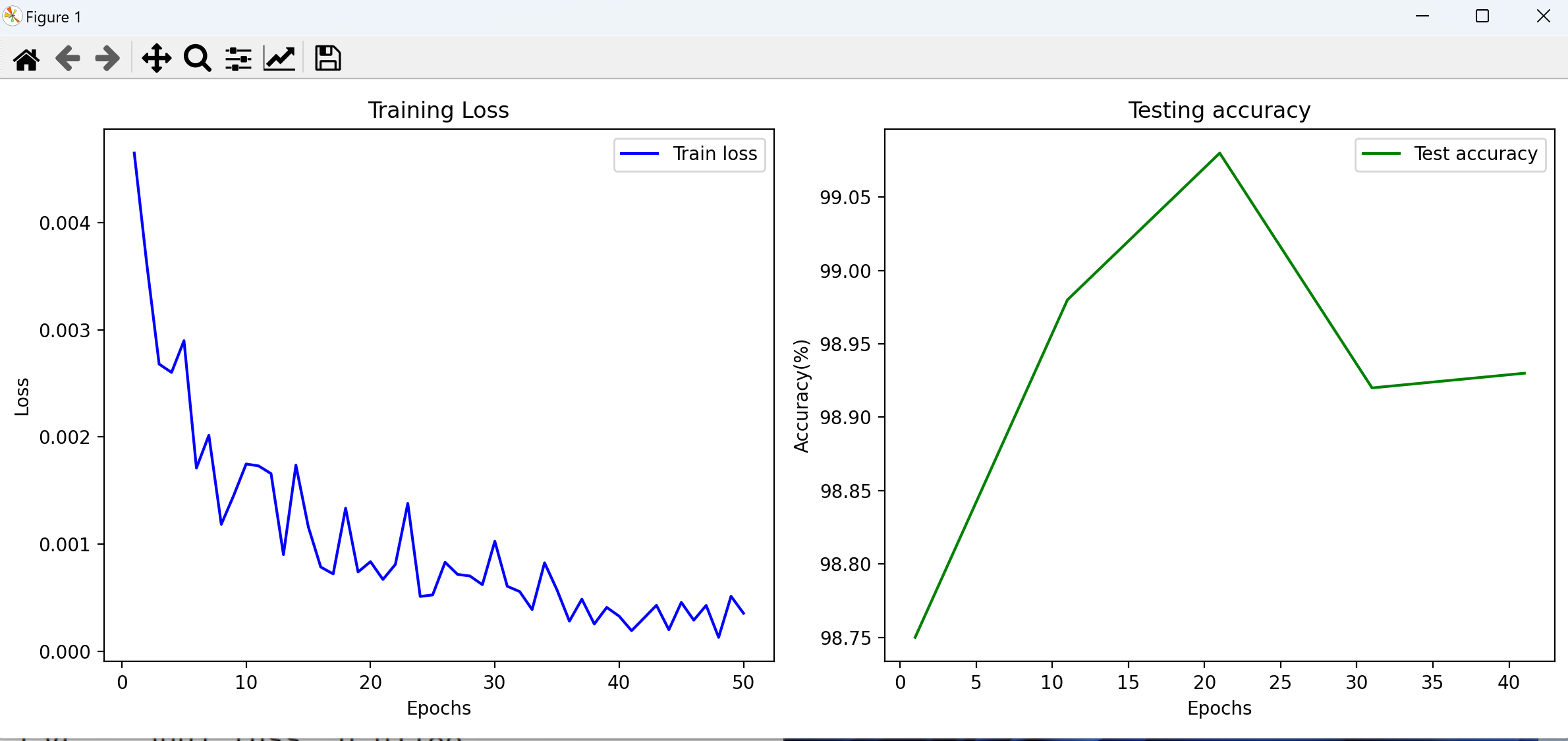
def plot_training_history():
epochs = range(1,len(train_losses)+1)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,5))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(epochs,train_losses,label='Train loss',color='blue')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs[::10], test_accuracies, label='Test accuracy', color='green')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy(%)')
plt.title('Testing accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(50):
train(epoch)
if epoch % 10 == 9 :
test()
plot_training_history()
|